Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What Is a Performance Appraisal Spider Chart?
- Benefits of Using Spider Charts for Employee Evaluation
- Key Components of Performance Spider Charts
- How to Create Effective Performance Spider Charts
- Implementing Spider Charts in Your Performance Review Process
- Spider Chart Examples in Different HR Functions
- Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using Performance Spider Charts
- Software Tools for Creating Performance Spider Charts
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Additional Resources
Introduction
Effective performance management is crucial for organizational success. HR professionals and managers are constantly seeking more intuitive, fair, and comprehensive methods to evaluate employee performance. Performance appraisal spider charts (also known as radar charts or web charts) offer a powerful solution by visualizing employee competencies across multiple dimensions in a format that's both insightful and easy to understand.
As an HR consultant who has implemented performance systems for over 50 organizations, I've seen firsthand how spider charts can transform the performance review process from a dreaded annual event into a constructive, development-focused conversation. According to a Harvard Business Review study, employees are 43% more likely to understand and accept feedback when it's presented visually rather than in text-only formats.
This comprehensive guide will show you exactly how to implement spider charts in your performance appraisal system to improve clarity, engagement, and developmental outcomes.
What Is a Performance Appraisal Spider Chart?
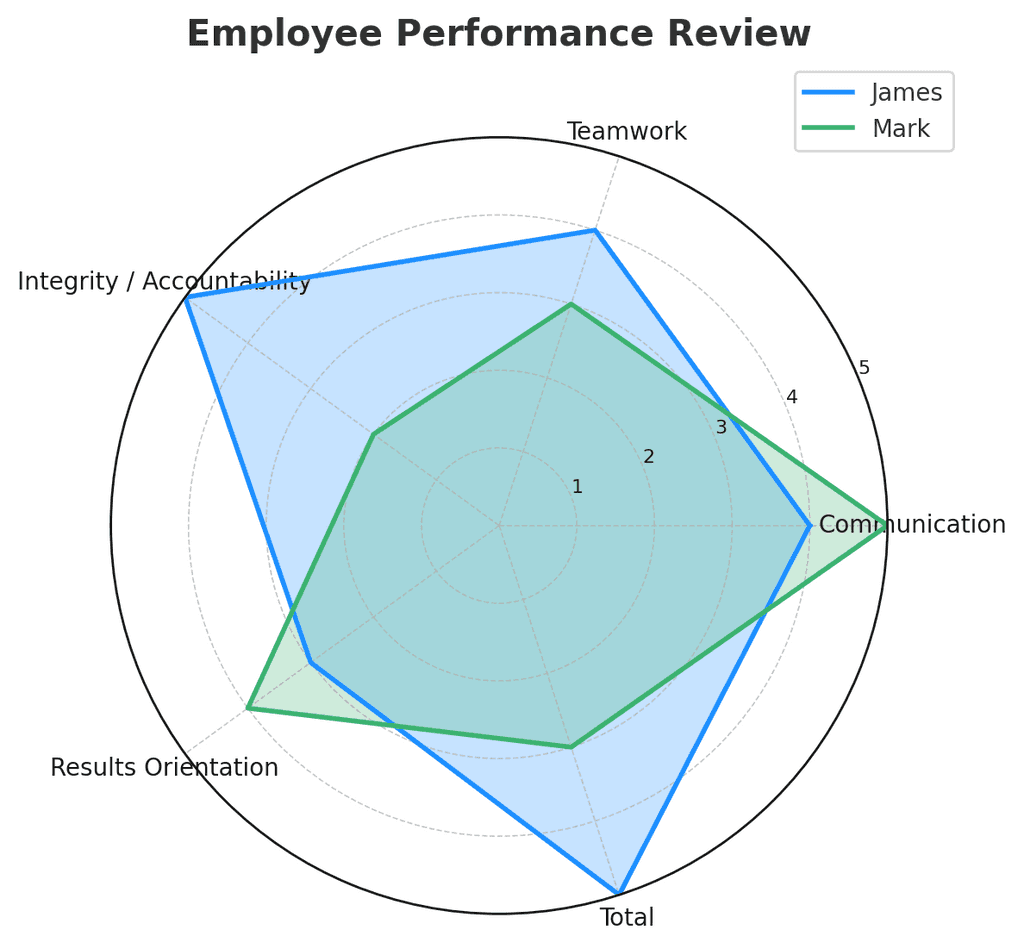
A performance appraisal spider chart is a visual tool that plots an employee's performance across multiple competencies or skill dimensions on a single graph. Each competency is represented by an axis radiating from a central point, creating a web-like or star-shaped visualization. The employee's rating on each competency is plotted along these axes, and when these points are connected, they form a polygon that represents the employee's overall performance profile.
Performance spider charts excel at:
- Displaying ratings across multiple performance dimensions simultaneously
- Highlighting strengths and development areas at a glance
- Comparing an employee's self-assessment with manager evaluations
- Tracking performance improvements over time
- Visualizing gaps between current performance and expected standards
The intuitive visual format makes performance discussions more concrete and helps both managers and employees quickly identify patterns that might be missed in traditional numerical or text-based evaluations.
Benefits of Using Spider Charts for Employee Evaluation
Implementing spider charts in your performance review process offers numerous advantages over traditional methods:
Enhanced Clarity and Communication
- Provides a clear visual representation that instantly communicates performance patterns
- Reduces misunderstandings about performance expectations and assessments
- Facilitates more focused, productive performance discussions
- Makes complex multi-dimensional feedback easier to comprehend
Holistic Performance Overview
- Shows the complete performance picture rather than isolated metrics
- Reveals balanced or imbalanced skill development
- Prevents overemphasis on a single strength or weakness
- Encourages evaluation across all relevant competencies
Improved Goal Setting and Development Planning
- Clearly identifies areas for improvement
- Helps prioritize development activities based on visual gaps
- Creates a baseline for measuring future progress
- Connects performance reviews directly to development planning
Increased Employee Engagement and Ownership
- Makes feedback more objective and less threatening
- Encourages self-assessment and reflection when used with structured feedback templates
- Provides a shared visual language for performance discussions
- Increases employee buy-in to the evaluation process
Better Comparison and Benchmarking
- Facilitates fair comparison across team members using consistent dimensions
- Enables comparison against job requirements or organizational standards
- Supports more objective promotion and succession planning decisions
- Highlights team strengths and development needs for resource allocation
Key Components of Performance Spider Charts
To create effective performance appraisal spider charts, you need to understand their key components:
Competency Axes (Spokes) Each axis represents a distinct competency, skill, or performance dimension being evaluated. These radiate from the center point and should be clearly labeled. The number of axes corresponds to the number of competencies being assessed.
Rating Scale Each axis has its own scale, typically with the lowest rating at the center and the highest at the outer edge. For consistency and fair comparison, all axes should use the same rating scale (such as 1-5 or 1-10).
Performance Points The employee's ratings for each competency are plotted along the corresponding axes. When connected, these points form a polygon representing the complete performance profile.
Expected Performance Level Many effective performance spider charts include a line or shape indicating the expected performance level for the role, which may vary by competency.
Multiple Data Sets Performance spider charts often include multiple polygons on the same chart to show:
- Self-assessment vs. manager assessment
- Current performance vs. previous review period
- Individual performance vs. team average
- Performance vs. career progression requirements
Legend When comparing multiple data sets, a clear legend is essential to distinguish between them.
How to Create Effective Performance Spider Charts
Follow these steps to design and implement impactful performance spider charts:
1. Select Appropriate Competencies Choose competencies that are:
- Directly relevant to the role and aligned with job descriptions
- Measurable and observable through workplace behaviors
- Limited to a reasonable number (typically 6-10) to prevent visual clutter
- Consistent with your organization's values and performance framework
2. Develop Clear Rating Criteria For each competency:
- Create specific behavioral descriptions for each rating level
- Ensure rating definitions are objective and observable
- Provide examples of performance at different rating levels
- Train evaluators on consistent application of rating criteria
3. Design the Chart for Clarity
- Use consistent spacing between axes
- Arrange related competencies adjacent to each other
- Place the most critical competencies at the top for emphasis
- Include clear labels and a performance key
- Add gridlines to aid in reading values
4. Collect Multi-Source Feedback Enhance the validity of your performance data by:
- Incorporating self-assessment using the same competencies and scale
- Including peer feedback when appropriate
- Using 360-degree feedback templates for senior roles
- Collecting specific behavioral examples to support ratings
5. Prepare for Constructive Discussions Before performance review meetings:
- Share the completed spider chart with the employee in advance
- Provide guidance on how to interpret the visualization
- Encourage reflection on the patterns shown
- Prepare to discuss specific development actions for areas with lower ratings
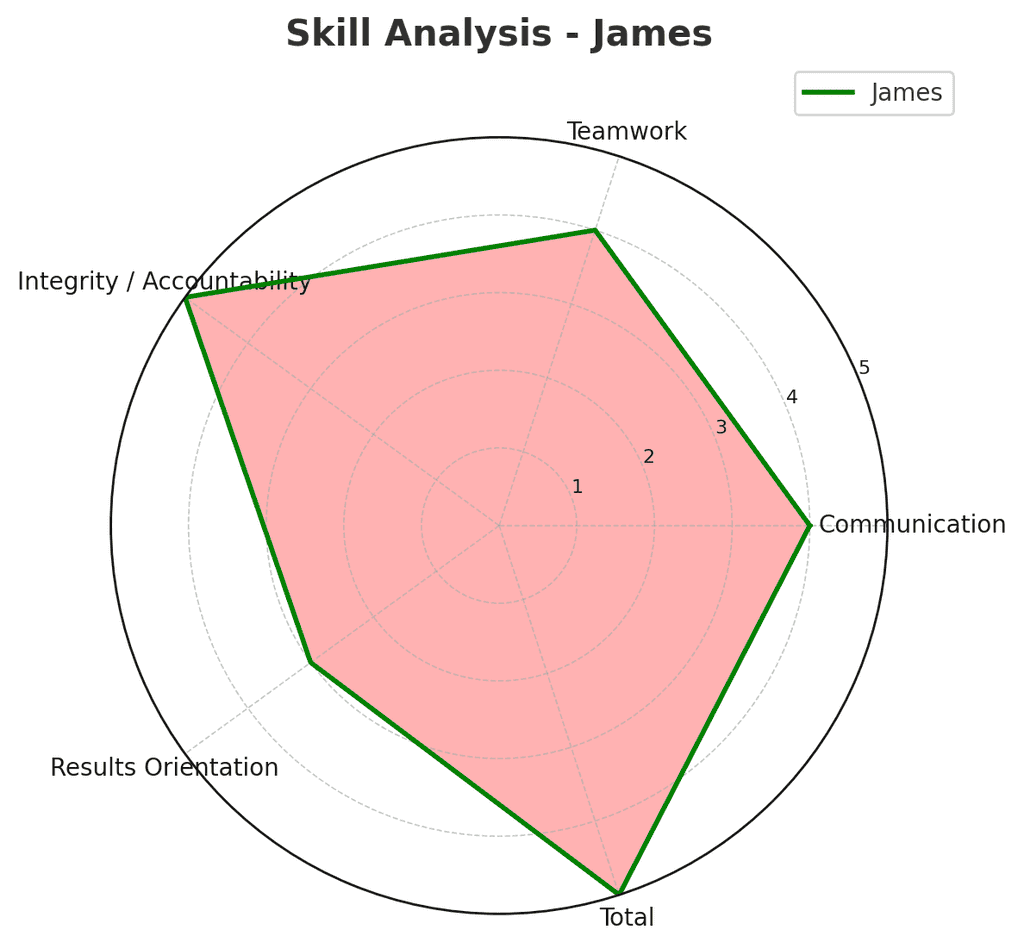
Implementing Spider Charts in Your Performance Review Process
Integrating spider charts into your existing performance management system requires thoughtful implementation:
Step 1: Align with Performance Framework Ensure the competencies used in your spider charts align with your organization's:
- Core values and cultural priorities
- Job descriptions and role expectations
- Career development pathways
- Strategic priorities and objectives
Step 2: Train Managers and Employees Provide comprehensive training on:
- How to interpret spider charts
- Using them as a coaching tool
- Avoiding common biases in ratings
- Conducting effective performance discussions using the visual format
- Turning negative feedback into constructive conversations using the visual aid
Step 3: Integrate with Development Planning Connect the spider chart directly to development actions by:
- Creating development plans that address the specific gaps identified
- Setting SMART goals aligned with improving lower-rated competencies
- Providing resources targeted to development needs
- Establishing check-in points to measure progress
Step 4: Create a Regular Review Cycle Establish a consistent rhythm for using spider charts:
- Quarterly light-touch reviews to track progress
- Annual comprehensive evaluations
- Project-based assessments for major initiatives
- Career progression evaluations for promotion considerations
Step 5: Gather Feedback and Refine Continuously improve your spider chart implementation by:
- Surveying managers and employees about the tool's effectiveness
- Refining competency definitions based on usage patterns
- Adjusting the number or type of dimensions evaluated
- Enhancing the visual design based on user feedback
Spider Chart Examples in Different HR Functions
Performance spider charts are versatile tools that can be used across multiple HR functions:
Performance Reviews The primary application is for comprehensive performance evaluations where spider charts provide a complete view of employee performance across all key competencies. For example, a software developer might be evaluated on technical skills, problem-solving, communication, collaboration, code quality, and timeliness.
Talent Development Spider charts help identify skill gaps and development priorities across individuals or teams. HR professionals use these visualizations to design targeted training programs and allocate development resources effectively. When combined with comprehensive 360-degree feedback processes, they provide a solid foundation for career development conversations.
Succession Planning When evaluating candidates for promotion, spider charts allow easy comparison of individuals against the competency requirements of higher-level positions. This visual format helps identify readiness gaps and create targeted development plans to prepare high-potential employees for future roles.
Team Composition and Development By overlaying spider charts of team members, managers can visualize the collective strengths and gaps within a team. This insight helps in assigning projects, forming balanced teams, and addressing team-wide development needs.
Recruitment and Selection Spider charts can be used during hiring to compare candidates against the ideal competency profile for a role, ensuring a good fit between the new hire's capabilities and job requirements.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using Performance Spider Charts
Even experienced HR professionals can make these common mistakes when implementing performance spider charts:
Overcomplicating with Too Many Dimensions Including too many competencies makes the chart cluttered and difficult to interpret. Limit your spider chart to 10 dimensions maximum, with 6-8 being ideal for most roles.
Using Inconsistent Rating Criteria When different evaluators interpret rating scales differently, comparisons become meaningless. Develop clear behavioral anchors for each rating level and train evaluators thoroughly.
Focusing Only on Weaknesses The visual nature of spider charts can sometimes overemphasize gaps or lower ratings. Ensure discussions address strengths as well as development areas, and consider the overall pattern rather than individual data points.
Neglecting Context and Explanation Spider charts are tools to facilitate discussion, not replace it. Always include narrative context, specific examples, and opportunities for dialogue when sharing performance visualizations.
Creating Artificial Symmetry Expectations Some managers mistakenly expect all employees to have balanced, symmetrical charts. In reality, different roles require different competency profiles, and individual variation is normal and valuable.
Implementing Without Proper Training Introducing spider charts without adequate preparation can lead to misinterpretation and resistance. Invest time in training both managers and employees on how to use and interpret these tools effectively.
Software Tools for Creating Performance Spider Charts
Several tools can help you create professional performance spider charts:
HR Performance Management Systems Many dedicated performance management platforms now include spider chart functionality built directly into their review process, with options for customization, comparison, and tracking over time.
Microsoft Excel Excel offers built-in radar chart functionality that's suitable for basic performance spider charts. While somewhat limited in customization, it's accessible and familiar to most HR professionals.
Tableau This powerful data visualization tool can create highly customizable spider charts with interactive features, allowing for sophisticated performance analytics and trend visualization.
Specialized HR Visualization Tools
- Culture Amp includes performance visualization capabilities
- 15Five offers visual performance snapshots
- Lattice provides visual performance and growth tracking
Online Chart Generators For simple implementation, tools like Canva, ChartGo, and Meta-Chart offer easy spider chart creation without requiring technical expertise.
Conclusion
Performance appraisal spider charts represent a powerful addition to your HR toolkit, offering a visual, intuitive approach to employee evaluation that enhances clarity, engagement, and development focus. When thoughtfully designed with appropriate competencies, consistent rating criteria, and clear visualization, they transform performance conversations from potentially adversarial encounters into constructive dialogues about growth and development.
Whether you're conducting annual reviews, quarterly check-ins, or career development discussions, spider charts can help you communicate complex performance information more effectively while encouraging employee ownership of development goals. By avoiding common implementation pitfalls and leveraging appropriate software tools, you can create a more transparent, fair, and development-oriented performance management system.
For HR professionals looking to modernize their approach to performance management, combining spider charts with comprehensive 360-degree feedback templates creates a powerful foundation for meaningful evaluation and targeted development planning.
The next time you prepare for performance reviews, consider how spider charts might help you deliver more impactful, actionable feedback that drives both individual growth and organizational success.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How many competencies should I include in a performance spider chart? A: While you could theoretically include any number, 6-8 competencies is typically optimal. This provides enough detail for a comprehensive evaluation while maintaining visual clarity. For entry-level positions, you might use fewer dimensions, while senior roles might require slightly more.
Q: Can spider charts be used for any type of role? A: Yes, spider charts are versatile and can be adapted for virtually any position by customizing the competencies evaluated. However, the specific dimensions will vary significantly between roles (e.g., technical skills for developers vs. client relationship management for account executives).
Q: How do I prevent biases in performance ratings used in spider charts? A: Develop clear behavioral descriptions for each rating level, train evaluators on bias awareness, gather multi-source feedback using standardized templates, and review patterns of ratings across groups to identify potential systemic biases.
Q: Should employees see their spider charts before the performance discussion? A: Yes, sharing the completed spider chart before the meeting gives employees time to reflect on the visualization and come prepared for a more productive discussion. This approach supports a no-surprises philosophy that builds trust in the performance process.
Q: How can I use spider charts to track performance improvement over time? A: Create overlaid spider charts showing ratings from different review periods (e.g., current vs. previous year). This clearly visualizes progress and continued development areas. Many performance management systems can automatically generate these comparison visualizations.
Q: How do spider charts work with numerical or objective performance metrics? A: Spider charts work best for competency-based assessments but can incorporate objective metrics by converting them to the same rating scale. For example, a sales target achievement of 127% might convert to a 4.5 on a 5-point scale for the "sales performance" dimension.
Q: How can I use spider charts in a remote or hybrid work environment? A: Spider charts are especially valuable for remote employees as they provide clear visual communication about performance that transcends distance. Use digital sharing tools during video performance discussions to review the charts together, and ensure remote managers are well-trained on conducting effective visual feedback sessions.